On average, Vicodin stays in your system for around 20 hours. However, drug tests can detect it for days or even months, depending on the method.
In this article, we’ll break down detection windows for blood, urine, saliva, and hair, plus the factors that influence elimination.
What Is Vicodin?
Vicodin is a potent opioid medication prescribed to treat moderate-to-severe pain resistant to non-opioid pain relievers. As a combination drug, it contains two active ingredients:
- Acetaminophen, an over-the-counter medication used to manage mild-to-moderate pain and treat fever
- Hydrocodone, a semi-synthetic derivative of codeine or thebaine, alkaloids naturally occurring in opioid poppy plants
Vicodin® is one of the brand names for generic acetaminophen/hydrocodone medication, which is also sold under some other brand names, including Norco®, Lortab®, and Lorcet®.
Brand-name Vicodin® comes in tablets containing 300 mg acetaminophen and 5 mg, 7.5 mg, or 10 mg hydrocodone, marketed as Vicodin®, Vicodin ES®, and Vicodin HP®, respectively. Meanwhile, generic acetaminophen/hydrocodone is also available as a liquid.

Acetaminophen/hydrocodone was the most commonly prescribed opioid in 2021. However, like any opioid medication, Vicodin has a high potential for opioid abuse, dependence, and addiction.
Although it was initially treated as a Schedule III controlled substance, Vicodin was reclassified as a Schedule II controlled substance in 2014. Nevertheless, it remains a popular street drug, with Vikes and Fluff being some of its most common street names.
To reduce the risks associated with Vicodin use, it is imperative to take the medication precisely as prescribed. Long-term hydrocodone use also increases the risk of addiction, dependence, and overdose, which is why it is not recommended to take Vicodin for chronic pain treatment.
How Does Vicodin Affect Your Body?
Vicodin affects the body by interacting with the opioid receptors in the central nervous system (CNS). Once consumed, it binds to these receptors, disrupting the transmission of pain signals between the body and the brain, which alters the perception of pain. Vicodin typically starts working within around 30 minutes of ingestion, with effects lasting for 4–8 hours.
While pain relief is the primary effect of Vicodin, it can also induce feelings of deep relaxation and euphoria by triggering a surge of dopamine in the brain. This further increases the risk of opioid abuse and addiction, as people are naturally wired to repeat actions that stimulate dopamine release.
Besides pain relief, relaxation, and euphoria, Vicodin can cause various side effects, ranging from mild to potentially life-threatening.
Common Vicodin Side Effects
- Itchy skin
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Dry mouth
- Drowsiness
- Constipation
- Blurred vision
- Trouble urinating
- Nausea and vomiting
While some of these may resolve independently, others may require medical attention. Therefore, it’s best to inform your doctor about any side effects you experience while taking this medication.
Vicodin Half-Life
Hydrocodone, the active opioid in Vicodin, has an average half-life of about 3.8 hours. This means it takes roughly 20 hours for most of the drug to leave the body. However, it takes five half-lives on average to fully clear opioids out of the system, and Vicodin is no exception.
How Long Does Vicodin Stay in Your System?
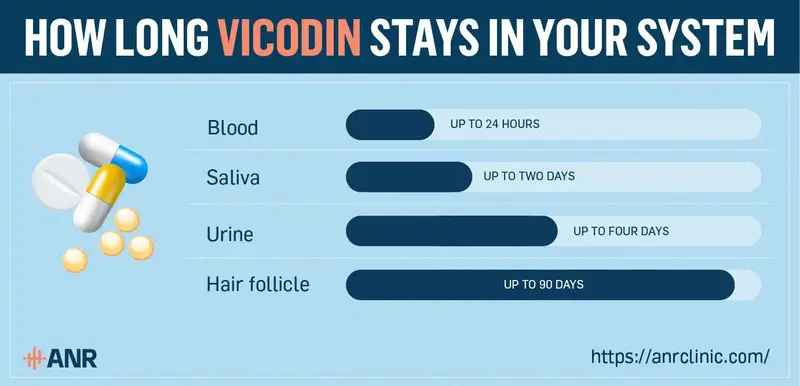
Vicodin stays in your system for around 20 hours, as the half-life of Vicodin is roughly four hours.
However, some drug tests may detect traces of its active opioid ingredient (hydrocodone) even months after the last dose, while others may only detect it for a day or two.
Let’s discuss the Vicodin detection times for blood, saliva, urine, and hair tests.
Blood Test Detection
Vicodin remains detectable in blood samples for up to 24 hours after the last dose. While blood tests are quite accurate, they have the shortest detection window for Vicodin. They are also more invasive and expensive than other forms of drug testing.
Saliva Detection Timeline
Vicodin can be detected in saliva samples for around 48 hours following the last dose. Most saliva tests are performed by sending an oral swab to the laboratory for inspection, and they are usually quite reliable and non-invasive.
Urine Testing Window
Vicodin is detectable in urine for up to four days after the last dose. Urine tests are quite popular, as they are easy to administer, have a relatively long detection window compared to blood and saliva tests, and are usually fairly affordable.
Hair Follicle Testing
Vicodin stays in the hair for up to 90 days after taking the last dose. Hair follicle tests are conducted on a 1.5-inch hair sample containing the follicle. Since these tests can detect whether you’ve used Vicodin in the last three months, they have the longest detection window but can be rather costly.
When Might It Be Undetectable?
In some cases, Vicodin may be undetectable in drug tests.
For instance, after 4+ days, urine samples usually won’t show traces unless you’ve been using heavily. Blood and saliva tests typically clear within 1–2 days. Hair follicle tests, however, are much harder to avoid since they can detect even one-time use for up to 90 days.
Which Factors Determine How Long Vicodin Stays in Your System?
Let’s examine several key factors that determine how long Vicodin stays in your system:
- Liver and kidney health. These are among the key factors that determine how long Vicodin stays in your system, as hydrocodone is metabolized mainly in the liver and primarily undergoes renal excretion. Impaired liver or kidney function may cause Vicodin to stay longer in your system, increasing the risk of opioid toxicity. The hydrocodone/acetaminophen combination, in particular, has been linked to acute liver injury and may not be suitable for those with liver disease.
- Metabolism. The faster your metabolism is, the less time your body will need to break down Vicodin and flush it out. Body composition, age, physical activity level, diet, and other factors that may affect your metabolic rate can also impact the elimination of Vicodin.
- Extent of Vicodin use. The dosage, frequency, and duration of opioid use play an important role in determining how long Vicodin stays in your system. Put simply, your body will have an easier time processing and eliminating Vicodin if you’ve been taking it in minimal doses for a short time as opposed to in large doses for a prolonged period.
- Use of other substances. Certain substances, including prescription drugs and herbal supplements, may hinder your body’s ability to metabolize and eliminate Vicodin effectively. Never take Vicodin with other substances your doctor hasn’t approved of, as this may also increase the risk of unwanted side effects, Vicodin overdose, and even death.
Vicodin Addiction vs. Vicodin Dependence
Vicodin addiction and Vicodin dependence are two distinct yet often co-occurring conditions that anyone taking this medication risks developing. Let’s break down these two notions:
| Aspect | Vicodin Dependence | Vicodin Addiction (OUD) |
| Primary Nature | Physical dependence | Primarily psychological |
| Who Can Develop It | Anyone taking Vicodin for extended time will eventually develop | Those who lose control over their impulses |
| Prescription Use | Even those who take Vicodin as prescribed can become dependent | Cannot stop taking even when it negatively affects life |
| Brain Changes | Brain stops producing endorphins and creates more opioid receptors | Not specified in provided information |
| Key Signs | Tolerance (usual dose no longer suffices) Opioid withdrawal symptoms Need to increase dosage to feel effects | Loss of control over impulses Cannot stop taking despite negative effects |
| Withdrawal Symptoms | Vomiting, body aches, cravings, other uncomfortable symptoms | Not specifically detailed for addiction |
| Daily Function | Have to rely on it to function normally | Cannot function normally due to loss of control |
| Impact on Life | Absence of drug leads to withdrawal symptoms | Negatively affects relationships, careers, and so forth |
| Relationship | Can develop into Vicodin addiction if left untreated | Develops from untreated Vicodin dependence |
| Risk Progression | May lead to addiction (OUD) | May lead to illicit drug use and increase overdose/death risk |
If left untreated, Vicodin dependence can develop into Vicodin addiction, also known as opioid use disorder (OUD). Sadly, those addicted to opioids lose control over their impulses and cannot stop taking them, even when it negatively affects their relationships, careers, and so forth.
Given that prescription drug addiction may lead to illicit drug use and significantly increase the risk of opioid overdose and death, getting professional opioid addiction treatment is of utmost importance.
Most Common Vicodin Withdrawal Symptoms

Vicodin withdrawal symptoms occur when people dependent on this medication attempt to quit it or reduce their dosage, especially suddenly.
The most common Vicodin withdrawal symptoms include:
- Anxiety
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Yawning
- Vomiting
- Shivering
- Depression
- Dilated pupils
- Loss of appetite
- Excessive sweating
- Muscle and joint aches
- Difficulty falling or staying asleep
- Changes in blood pressure and heart rate
- Flu-like symptoms, such as fever and runny nose
Since the half-life of Vicodin is relatively short, you may experience the first withdrawal symptoms within just 12–24 hours after your last Vicodin dose. While these symptoms typically subside within a week, it’s not unusual for people to suffer from cravings, insomnia, and depression for weeks and even months after discontinuing Vicodin.
Importantly, going through Vicodin withdrawal puts you at a high risk of relapse. If you relapse, even your usual dose may be potent enough to cause a potentially fatal opioid overdose. This, coupled with the fact that Vicodin withdrawal can lead to life-threatening complications like extreme dehydration, explains why you should never quit Vicodin without medical supervision.
Treatment for Vicodin Dependence
Accelerated Neuro-Regulation (ANR) is a medical treatment for opioid dependence that focuses on re-regulating the brain’s endorphin-receptor system. Unlike traditional methods that mainly address withdrawal, ANR aims to target the neurochemical imbalance underlying opioid dependence. The procedure is performed in a hospital setting under medical supervision and is tailored to each patient’s health condition. Its safety and effectiveness have been supported by scientific research.
To get started with ANR, contact us today and book a free consultation.
Key Takeaways
While the general answer to “How long does Vicodin stay in your system?” is 20 hours, the rate at which the body processes and clears this medication largely depends on your health, metabolism, the extent of Vicodin use, and whether or not you’re taking any other substances.
Now, let’s reiterate the key points we covered:
- Vicodin is a prescription opioid pain medication made up of acetaminophen and hydrocodone.
- Vicodin can be detected in blood for around 24 hours, in saliva for about 48 hours, in urine for up to four days, and in hair follicle samples for up to three months after ingestion.
Additional Information
Norco vs. Vicodin: Risks, Side Effects, and Treatment Solutions
